Table of Contents
Download Planning for a New Northeast Corridor:

Download The Hudson Terminal Plan:

Download the Trends & Opportunities Report:

Trends in Metropolitan Transit
Rail on the Rise
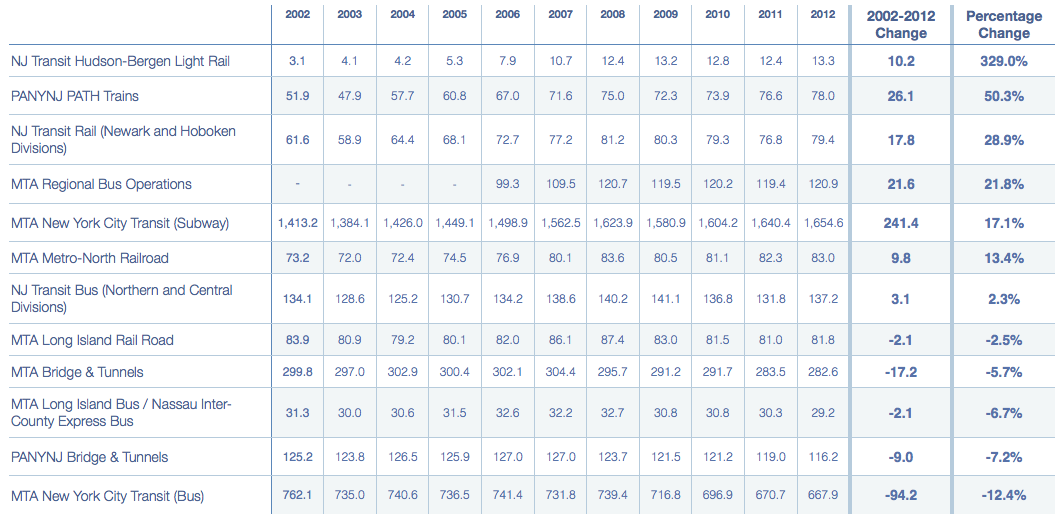
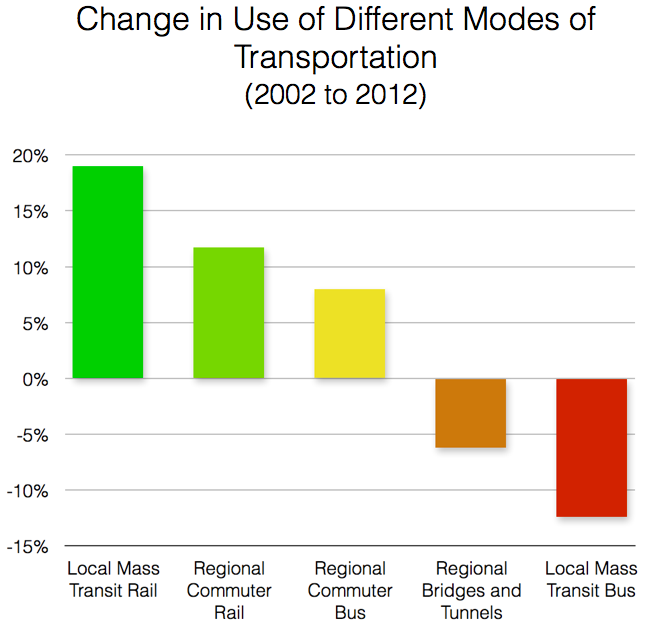
From 2002 to 2012, the New York metropolitan area has seen substantial ridership growth in both local and regional rail systems. In terms of local mass transit rail, the New York Subway system added the greatest number of annual riders since 2002 at 241.4 million, which represented a 17.1% rise in ridership over ten years. Hudson-Bergen Light Rail, however, had the most dramatic gains by percentage, growing 329% since 2002 and gaining over 10 million annual passengers. Ridership growth was also very high for the PATH system and Newark Light Rail, which had ridership growth of 50.3% and 42.5% respectively. Overall, local mass transit rail ridership increased by 279.4 million annual riders over the past ten years. Regional commuter rail ridership, which includes MTA LIRR, MTA Metro-North, and NJ Transit (Hoboken and Newark divisions), also increased by 25.5 million annual passengers, or 11.7% growth, since 2002. Growth has been less apparent for regional commuter bus systems, which grew by only 8% over ten years. Included in this growth, however, is a ten-year loss of 2.1 million annual riders using Nassau Inter-County Express Bus service, formerly known as MTA Long Island Bus.
Annual Ridership by Transit Mode (millions of passengers)
Vehicle crossings over the metropolitan region’s bridges and tunnels declined by 26.2 million annual trips over ten years, amounting to a net decrease of 6.2%. However, the steepest decline in transit ridership over the past ten years has come from local bus services, presumably because of a shift in transit mode preference as riders choose to take advantage of newer light-rail networks and local mass transit improvements. The MTA’s NYCT Bus service alone lost 94.2 million annual riders since 2002, amounting to a net decrease of over 12%.
In sum, more and more riders are choosing to travel by rail around the metropolitan region, with the greatest increases coming from local and regional routes in northern New Jersey. In addition, New York City subway service has added nearly a quarter of a billion annual riders since 2002. In contrast, use of the metropolitan region’s roads, whether by bus or by automobile, has generally declined over the past decade.